Database Pessimistic Locking
Index
Several Core Key Points
The Relationship Between autocommit and begin / start transaction
- Different scope of effect:
autocommitis a database-level property in the InnoDB engine, whereasbeginandstart transactionare globally effective. OnceSET AUTOCOMMIT=0is used to disable auto-commit, all transactions within the database will not automatically commit unless you manually execute acommitorrollbackstatement for each transaction. On the other hand,start transactionandbegin/commitcan only control a specific transaction.
- Different priorities:
start transactionandbegin/commithave a higher priority thanautocommit. That is, even ifautocommit=1, if a statement explicitly declares the start of a transaction (begin/commit), you still need to manually commit or rollback.
Difference Between Exclusive Lock and Shared Lock
- Shared Lock (
lock in share mode): After the lock is acquired, another thread can only read the data, but cannot modify it. - Exclusive Lock (
select ... for update): Once the lock is acquired, another thread cannot read or modify the data.
Note: If one thread executes a
for updateto lock a row of data, other threads can still read the data normally as long as the SQL query does not includefor update.
【Warning】
If the condition for for update does not hit an index, it will lock the entire table!!!
The table below shows the lock results when different types of indexes are hit and whether the query result is empty.
| Primary Key Index | Regular Index | Is the Result Set Empty? | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | row lock |
| ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | row lock |
| ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | table lock |
Scope of Use
- The table must be a mysql InnoDB table
- Transactions (transaction) must be enabled
Usage
Shared Lock and Pessimistic Lock Code Example
Exclusive Lock Controller
/**
* 使用悲观锁(排它锁)创建订单.
* @param LockRequest $request 请求验证器
* @return array ['code' => '200', 'msg' => 'ok', 'status' => true, 'data' => []]
*/
#[PostMapping(path: 'pessimism/for_update')]
#[Scene(scene: 'create_order')]
public function createOrderByForUpdate(LockRequest $request): array
{
$gid = intval($request->input('gid'));
$num = intval($request->input('number'));
$uid = $this->jwtPayload['data']['uid'];
$orderNo = $this->service->createOrderWithForUpdate($uid, $gid, $num);
return $this->result->setData(['oder_no' => $orderNo])->getResult();
}
Exclusive Lock Logic
/**
* 悲观锁创建订单(排它锁).
* @param int $uid 用户id
* @param int $gid 商品id
* @param int $number 购买数量
* @return string 订单编号
*/
public function createOrderWithForUpdate(int $uid, int $gid, int $number = 1): string
{
// 开启事务
Db::beginTransaction();
try {
$orderNo = '';
/** 加上排它锁 @var Goods $goodInfo */
$goodInfo = Goods::query()->where(['id' => $gid])->lockForUpdate()->first();
// 商品不存在
if ($goodInfo === null) {
throw new BusinessException(...self::getErrorMap(ErrorCode::GOOD_NOT_FOUND));
}
// 库存不足
if ($goodInfo->stock < $number) {
throw new BusinessException(...self::getErrorMap(ErrorCode::GOOD_STOCK_EMPTY, [$goodInfo->name]));
}
// 创建订单
$orderNo = Math::getUniqueId();
(new Orders([
'uid' => $uid,
'gid' => $gid,
'order_no' => $orderNo,
'number' => $number,
'payment_money' => Math::mul($goodInfo->price, $number),
]))->save();
// 扣减库存
$goodInfo->stock = $goodInfo->stock - $number;
$goodInfo->save();
Db::commit();
} catch (Throwable $e) {
Db::rollBack();
}
if ($orderNo === '') {
throw new BusinessException(...self::getErrorMap(ErrorCode::STOCK_EMPTY));
}
return $orderNo;
}
Shared Lock Controller
/**
* 使用悲观锁(共享锁)创建订单.
* @param LockRequest $request 请求验证器
* @return array ['code' => '200', 'msg' => 'ok', 'status' => true, 'data' => []]
*/
#[PostMapping(path: 'pessimism/share_mode')]
#[Scene(scene: 'create_order')]
public function createOrderByShareMode(LockRequest $request): array
{
$gid = intval($request->input('gid'));
$num = intval($request->input('number'));
$uid = $this->jwtPayload['data']['uid'];
$orderNo = $this->service->createOrderWithShareMode($uid, $gid, $num);
return $this->result->setData(['oder_no' => $orderNo])->getResult();
}
Shared Lock Logic
/**
* 悲观锁创建订单(共享锁).
* @param int $uid 用户id
* @param int $gid 商品id
* @param int $number 购买数量
* @return string 订单编号
*/
public function createOrderWithShareMode(int $uid, int $gid, int $number = 1): string
{
// 开启事务
Db::beginTransaction();
try {
/** 加上共享锁 @var Goods $goodInfo */
$goodInfo = Goods::query()->where(['id' => $gid])->sharedLock()->first();
// 商品不存在
if ($goodInfo === null) {
throw new BusinessException(...self::getErrorMap(ErrorCode::GOOD_NOT_FOUND));
}
// 库存不足
if ($goodInfo->stock < $number) {
throw new BusinessException(...self::getErrorMap(ErrorCode::GOOD_STOCK_EMPTY, [$goodInfo->name]));
}
// 创建订单
$orderNo = Math::getUniqueId();
(new Orders([
'uid' => $uid,
'gid' => $gid,
'order_no' => $orderNo,
'number' => $number,
'payment_money' => Math::mul($goodInfo->price, $number),
]))->save();
// 扣减库存
$goodInfo->stock = $goodInfo->stock - $number;
$goodInfo->save();
Db::commit();
} catch (Throwable $e) {
$orderNo = '';
Db::rollBack();
}
if ($orderNo === '') {
throw new BusinessException(...self::getErrorMap(ErrorCode::STOCK_EMPTY));
}
return $orderNo;
}
Notes
【Warning】
- Pay attention to the locking condition, it must use an index, preferably the primary key index, because if the index is not hit, the entire table will be locked.
- When an explicit transaction locks a row of data, other implicit
updateoperations on that row will also wait for the lock, because a singleupdateSQL is also a transaction. Don't assume that otherupdate statementsoutside ofBEGINandCOMMITwon't wait. - It is best not to use
MySQLfor explicit lock operations. The database should focus more on being a data storage solution.
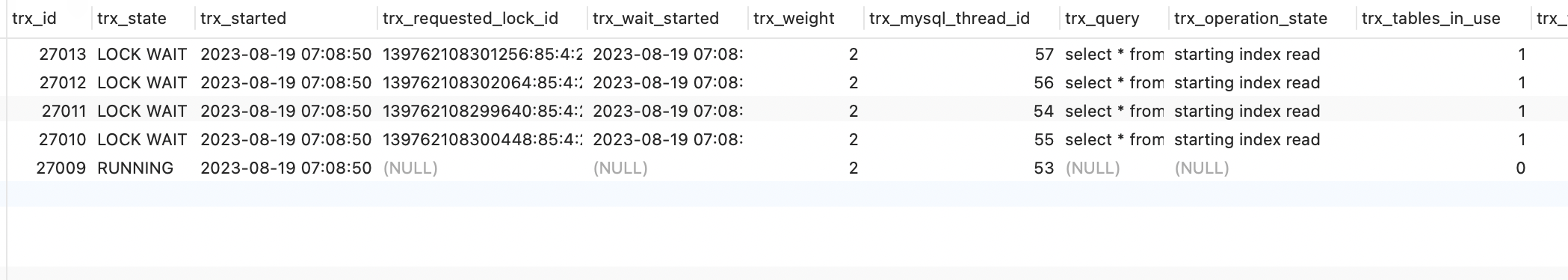
Viewing Transactions and Locks
Viewing Transaction and Lock Status
【Additional Information】
You can view the transaction and lock status through the
information_schema.INNODB_TRXtable. Field descriptions forinformation_schema.INNODB_TRX

// Viewing Transaction and Lock Status
select * from information_schema.innodb_trx
Usage Cases
- Low concurrency, relatively independent (attempt to lock rows that are not updated by other operations), and strong consistency database operations.